El estiércol de gallina es un fertilizante orgánico de alta calidad que ofrece numerosos beneficios para el crecimiento de las plantas. Contiene nutrientes esenciales como nitrógeno, fósforo, potasio y otros elementos que brindan un soporte nutricional completo. Sin embargo, antes de utilizar el estiércol de gallina como fertilizante, es fundamental realizar un proceso de fermentación completo.

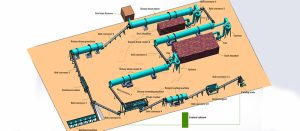
El primer paso importante es deshidratar la gallinaza antes de compostarla. La deshidratación reduce el contenido de humedad de la gallinaza, lo que la hace más adecuada para el compostaje. Nuestra deshidratadora de tornillo puede ayudarte a reducir el contenido de humedad de la gallinaza a un nivel óptimo de 30%-40%, cumpliendo así con los requisitos previos al compostaje.

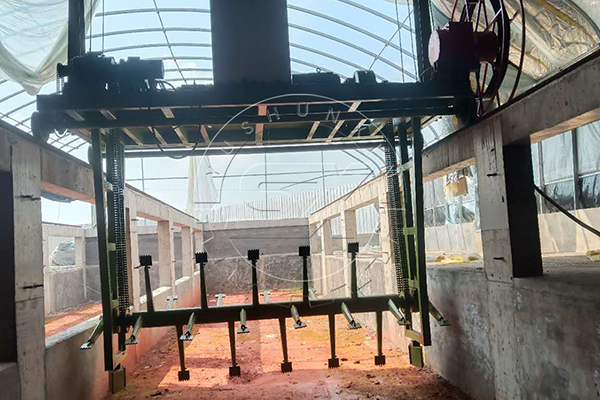
Durante el proceso de fermentación, es esencial voltear regularmente el estiércol. Esto crea canales que mejoran la circulación de aire, lo que favorece el contacto entre el oxígeno y el estiércol, proporcionando un entorno respiratorio óptimo para el crecimiento y la actividad de los microorganismos beneficiosos.
Para satisfacer tus necesidades, ofrecemos diferentes opciones de volteadores de composta. Nuestro volteador de composta de ranura tiene un ancho de volteo que varía entre 3 y 30 metros, y una profundidad de volteo que puede llegar a 0,8-1,8 metros. También contamos con un volteador de composta móvil, ideal para la producción de compostaje de gallinaza a pequeña y mediana escala.

Durante el proceso de fermentación, puedes agregar una cantidad adecuada de paja o rastrojo. La adición de paja ayuda a mejorar la estructura del montón de compost y proporciona una fuente adicional de carbono, esencial para el desarrollo saludable de los microorganismos descomponedores.
El abono orgánico completamente fermentado no tiene olor desagradable. Durante el proceso de fermentación, los microorganismos descomponen los materiales orgánicos, incluyendo el estiércol, y producen calor y dióxido de carbono como subproductos. A medida que se lleva a cabo una fermentación adecuada, los compuestos orgánicos se descomponen y se transforman en formas estables y más simples. Como resultado, el abono orgánico fermentado tiene un olor neutral o incluso un agradable olor terroso.
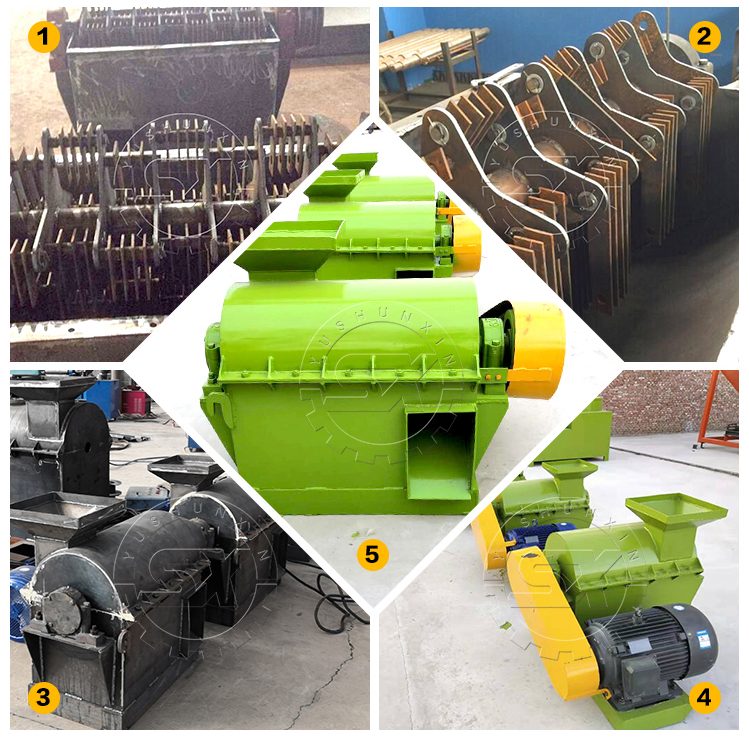
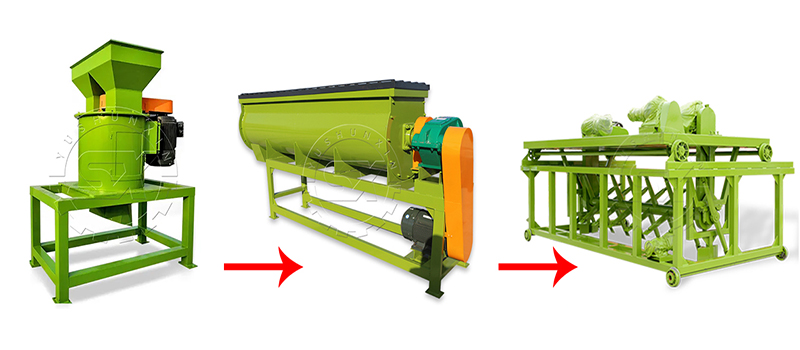
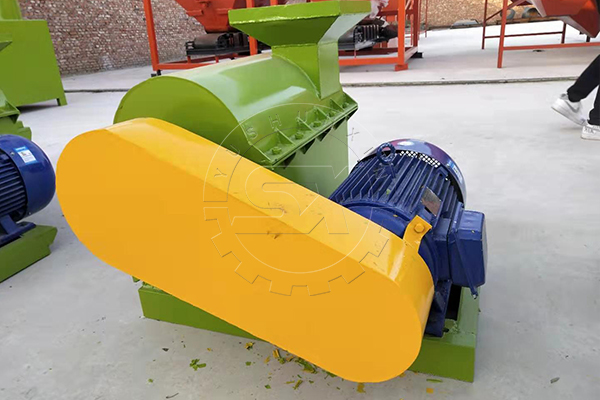
Si deseas producir más gránulos de abono orgánico, es necesario triturar y moler adecuadamente las materias primas antes de la granulación. Recomendamos utilizar una trituradora de materiales semihúmedos para este proceso. Nuestra trituradora utiliza cuchillas de doble capa para lograr una molienda más efectiva. Además, está equipada con rascadores para evitar que los materiales se peguen a las paredes.

Una vez que las materias primas están trituradas, puedes optar por envasar el abono orgánico terminado directamente con una empacadora si deseas producir abono en polvo. Si prefieres producir gránulos, necesitarás una granuladora adecuada. La máquina de compactación de rodillos es una excelente opción para la producción de gránulos de abono orgánico a partir de estiércol de gallina. Esta máquina ofrece numerosas ventajas, como no requerir secado previo, funcionar a temperatura ambiente y permitir la producción de gránulos en una sola operación. Además, puedes ajustar su configuración para obtener el tamaño de gránulo deseado.
Finalmente, puedes utilizar nuestra máquina automática de embalaje para empacar los gránulos de abono de manera rápida y eficiente. Esta máquina asegura la hermeticidad y la apariencia ordenada de los productos, y te permite configurar las especificaciones y el peso del embalaje según tus necesidades.
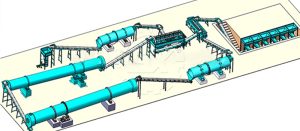
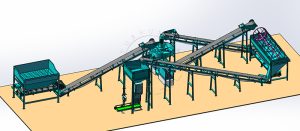
En resumen, la línea de obonos orgánicos de estiércol de gallina ofrece una solución completa para el proceso de fermentación y granulación de este fertilizante de alta calidad. Desde la deshidratación y el compostaje hasta la producción de gránulos y el empaque, nuestras máquinas están diseñadas para ayudarte a obtener los mejores resultados en la producción de abono orgánico a base de estiércol de gallina.